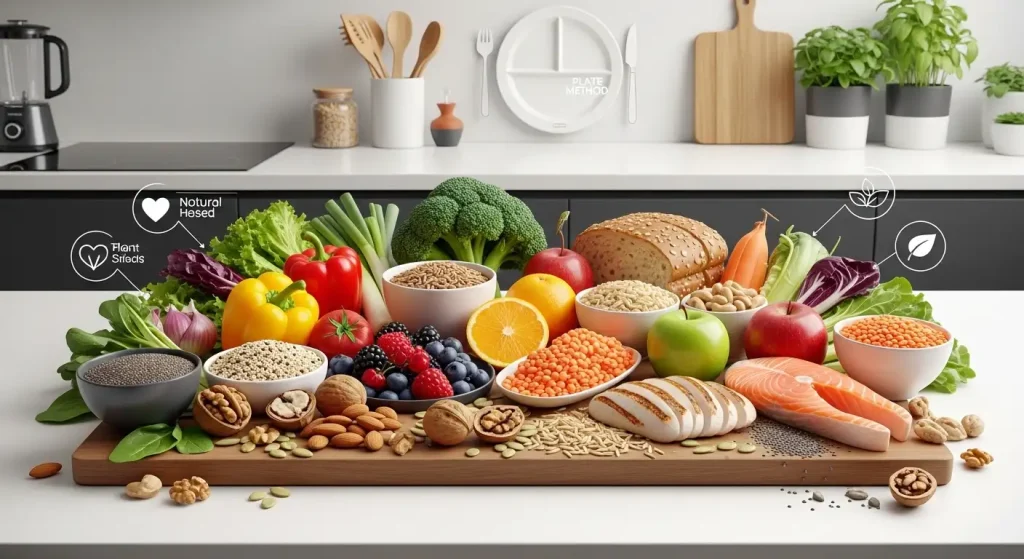
Understanding nutrition basics and adopting healthy eating habits are fundamental steps toward achieving optimal health and well-being. With countless diet trends and conflicting information available, mastering the core principles of nutrition basics helps you make informed decisions about your daily food choices. This comprehensive guide will provide you with evidence-based strategies for healthy eating that you can implement immediately to improve your overall health.
Discover Small European Towns Worth Visiting Instead of the Crowds
Why Nutrition Basics Matter for Your Health
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans provides advice on what to eat and drink to meet nutrient needs, promote health, and prevent disease. Understanding nutrition basics empowers you to create sustainable, healthy eating patterns that support your body’s needs throughout life.
Key benefits of mastering nutrition basics include:
- Disease Prevention: Reduced risk of heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy body weight through balanced nutrition
- Energy Optimization: Sustained energy levels throughout the day
- Mental Clarity: Better cognitive function and mood stability
- Longevity: Increased lifespan and improved quality of life
- Immune Support: Stronger immune system to fight off infections
Essential Macronutrients in Healthy Eating
Understanding Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are your body’s primary energy source and a crucial component of nutrition basics. Focus on complex carbohydrates that provide sustained energy and essential nutrients.
Best Carbohydrate Sources for Healthy Eating:
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, oats, whole wheat bread
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, chickpeas, peas
- Vegetables: Sweet potatoes, squash, corn, root vegetables
- Fruits: Berries, apples, bananas, citrus fruits
Protein for Optimal Health
Protein plays a vital role in muscle maintenance, immune function, and satiety. Understanding protein needs is fundamental to nutrition basics.
High-Quality Protein Sources:
- Lean Meats: Chicken breast, turkey, lean beef, fish
- Plant-Based: Tofu, tempeh, legumes, nuts, seeds
- Dairy: Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, milk
- Eggs: Complete protein with all essential amino acids
Healthy Fats in Your Balanced Diet
Contrary to past beliefs, healthy fats are essential for hormone production, brain function, and nutrient absorption.
Beneficial Fat Sources:
- Monounsaturated: Avocados, olive oil, nuts, seeds
- Polyunsaturated: Fatty fish, walnuts, flaxseeds, chia seeds
- Omega-3s: Salmon, sardines, mackerel, hemp seeds
Stress Management Techniques: 12 Proven Methods to Reduce Anxiety
Micronutrients: The Foundation of Nutrition Basics
Essential Vitamins for Healthy Eating
Vitamins support numerous bodily functions and are crucial components of nutrition basics.
| Vitamin | Function | Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A | Vision, immune function | Carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach |
| Vitamin C | Antioxidant, collagen synthesis | Citrus fruits, berries, bell peppers |
| Vitamin D | Bone health, immune support | Fatty fish, fortified foods, sunlight |
| B Vitamins | Energy metabolism, nerve function | Whole grains, leafy greens, eggs |
| Vitamin K | Blood clotting, bone health | Leafy greens, broccoli, Brussels sprouts |
Important Minerals for Optimal Health
Minerals support bone health, muscle function, and metabolic processes.
Key Minerals for Healthy Eating:
- Calcium: Dairy products, leafy greens, almonds, sardines
- Iron: Red meat, spinach, lentils, fortified cereals
- Magnesium: Nuts, seeds, whole grains, dark chocolate
- Potassium: Bananas, potatoes, beans, yogurt
- Zinc: Meat, pumpkin seeds, chickpeas, dairy
Retirement Planning Basics: Your Complete Guide to Financial Freedom
Creating a Balanced Diet: Practical Nutrition Basics
The Plate Method for Healthy Eating
The plate method simplifies nutrition basics by providing visual guidelines for balanced meals:
Ideal Plate Composition:
- Half the Plate: Vegetables and fruits (variety of colors)
- Quarter of the Plate: Lean protein sources
- Quarter of the Plate: Whole grain or starchy vegetables
- Added Elements: Healthy fats and dairy/dairy alternatives
Portion Control Strategies
Understanding proper portion sizes is fundamental to nutrition basics and maintaining a healthy weight.
Visual Portion Guides:
- Protein: Palm-sized portion (3-4 oz)
- Carbohydrates: Cupped hand portion (1/2 to 1 cup)
- Fats: Thumb-sized portion (1-2 tablespoons)
- Vegetables: Two cupped hands (1-2 cups)
Meal Planning for Sustainable Healthy Eating
Weekly Meal Planning Strategies
Effective meal planning supports consistent healthy eating and saves time and money.
Meal Planning Steps:
- Plan Weekly Menus: Include breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks
- Create Shopping Lists: Organize by food categories for efficiency
- Prep Ingredients: Wash, chop, and portion foods in advance
- Batch Cooking: Prepare large quantities of staples like grains and proteins
- Storage Solutions: Use proper containers for food safety and freshness
Smart Grocery Shopping for Nutrition Basics
You can master healthy eating by learning how to plan meals and shop smart, and by practicing healthy-cooking techniques.
Shopping Tips for Healthy Eating:
- Shop the perimeter of the store first (fresh foods)
- Read nutrition labels and ingredient lists
- Choose seasonal produce for better taste and value
- Buy frozen fruits and vegetables as nutritious alternatives
- Compare unit prices to find the best deals
How to Budget & Save Money Effectively: A Complete Guide
Hydration: The Overlooked Component of Nutrition Basics
Daily Water Requirements
Proper hydration is essential for nutrient transport, temperature regulation, and overall health.
Hydration Guidelines:
- General Rule: 8 glasses (64 oz) of water daily
- Active Individuals: Additional 16-24 oz for every hour of exercise
- Climate Considerations: Increase intake in hot or dry conditions
- Food Sources: Fruits, vegetables, and soups contribute to fluid intake
Beyond Water: Healthy Beverage Choices
Nutritious Drink Options:
- Herbal Teas: Antioxidant-rich and caffeine-free options
- Green Tea: Contains beneficial compounds and moderate caffeine
- Vegetable Juices: Nutrient-dense but watch sodium content
- Smoothies: Blend fruits, vegetables, and protein sources
Special Considerations in Healthy Eating
Age-Specific Nutrition Needs
Nutrition basics vary across different life stages, requiring adjustments to support optimal health.
Life Stage Considerations:
- Children: Focus on growth-supporting nutrients like calcium and protein
- Teenagers: Increased calorie needs and emphasis on iron and B vitamins
- Adults: Balanced approach with attention to chronic disease prevention
- Seniors: Higher protein needs and focus on nutrient-dense foods
Dietary Restrictions and Healthy Eating
Many people have dietary restrictions that require modified approaches to nutrition basics.
Common Dietary Adaptations:
- Vegetarian/Vegan: Focus on plant-based protein combinations and B12 supplementation
- Gluten-Free: Emphasize naturally gluten-free whole grains
- Dairy-Free: Include calcium-rich alternatives and fortified products
- Food Allergies: Read labels carefully and find suitable substitutions
How to Plan an Affordable Family Vacation
Common Nutrition Myths Debunked
Separating Fact from Fiction
Understanding evidence-based nutrition basics helps you avoid common misconceptions about healthy eating.
Debunked Nutrition Myths:
- Myth: Carbs are bad for you
- Fact: Complex carbohydrates are essential for energy and health
- Myth: All fats cause weight gain
- Fact: Healthy fats are necessary for optimal body function
- Myth: Supplements replace a balanced diet
- Fact: Whole foods provide superior nutrition with better absorption
Building Sustainable Healthy Eating Habits
The 80/20 Approach
Sustainable healthy eating follows the principle of making nutritious choices 80% of the time while allowing flexibility for the remaining 20%.
Implementation Strategies:
- Focus on progress, not perfection
- Allow occasional treats without guilt
- Plan for social situations and special occasions
- Listen to your body’s hunger and fullness cues
- Make gradual changes rather than dramatic overhauls
Mindful Eating Practices
Incorporating mindfulness into your meals enhances the healthy eating experience and improves digestion.
Mindful Eating Techniques:
- Eat without distractions (TV, phone, computer)
- Chew slowly and savor flavors
- Pay attention to hunger and satiety signals
- Express gratitude for your food
- Notice emotional triggers for eating
Ultimate Guide to Starting Your Home Vegetable Garden
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most important nutrition basics for beginners?
The most important nutrition basics for beginners include eating a variety of whole foods, following the plate method (half vegetables/fruits, quarter protein, quarter whole grains), staying hydrated with adequate water intake, and practicing portion control. Focus on adding more vegetables, choosing whole grains over refined ones, and including lean proteins in each meal. Start with small, sustainable changes rather than dramatic dietary overhauls.
How can I maintain healthy eating habits with a busy schedule?
Maintaining healthy eating with a busy schedule requires strategic meal planning and preparation. Dedicate time each week to plan meals, create shopping lists, and prep ingredients. Batch cook proteins and grains, keep healthy snacks readily available, and consider nutritious convenience options like pre-cut vegetables and canned beans. Focus on simple, balanced meals that can be prepared quickly or made ahead of time.
Do I need supplements if I follow good nutrition basics?
Most people can meet their nutritional needs through a well-balanced diet following proper nutrition basics. However, certain populations may benefit from specific supplements, including vitamin D (especially in low-sunlight areas), vitamin B12 (for vegans), iron (for people with deficiency), and omega-3s (for those who don’t eat fish). Consult with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian to determine if supplements are necessary for your individual needs.
How do I transition from an unhealthy diet to healthy eating?
Transitioning to healthy eating should be gradual and sustainable. Start by adding one serving of vegetables to each meal, replacing refined grains with whole grains, and choosing water over sugary drinks. Make one healthy swap per week, such as choosing brown rice instead of white rice or snacking on fruits instead of processed snacks. Focus on adding nutritious foods rather than restricting everything, which makes the transition more positive and maintainable.
Mindfulness Techniques for Reducing Everyday Stress
Start Your Healthy Eating Journey Today
Understanding nutrition basics is the first step toward transforming your health through better food choices. Remember that healthy eating is a journey, not a destination, and small consistent changes lead to significant long-term benefits.
Begin by implementing one or two strategies from this guide, such as following the plate method or planning weekly meals. As these become habits, gradually incorporate additional nutrition basics to build a comprehensive approach to healthy eating.
Ready to take your nutrition to the next level? Discover personalized meal plans, nutrition tracking tools, and expert guidance designed specifically for your health goals and dietary preferences. [Insert affiliate link here] offers comprehensive nutrition programs that make implementing these nutrition basics simple and sustainable, with step-by-step guidance and ongoing support for lasting success.
Remember: Healthy eating is a lifelong practice that supports your overall well-being. Be patient with yourself as you learn and implement new nutrition basics, and celebrate the positive changes you’re making for your health.